See also
Antimicrobial guidelines
Key points
- Steady-state vancomycin concentrations are required to ensure that the target therapeutic range is achieved. The therapeutic target is dependent on the patient’s age and administration method
- Administer vancomycin intravenously (IV) over at least 1 hour for intermittent infusions. Rapid infusion may cause vancomycin infusion reaction
- Seek pharmacist or specialist advice for infants and children with impaired renal function, receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or renal replacement therapy
This guideline is intended for infants and children with normal renal function
Background
Terms used in this CPG
- Steady-state: the time when vancomycin amount in the blood is constant or at equilibrium. For vancomycin, this occurs at least 24 hours after vancomycin treatment has commenced
- All vancomycin concentrations (trough or random) should be taken once vancomycin exposure in the blood reaches steady-state. Measuring the concentration earlier may lead to incorrect dose adjustments
- Steady-state trough concentration: trough concentration (taken within 30 minutes of a due dose) taken at least 24 hours after commencement of vancomycin. This is used for intermittent dosing
- Steady-state concentration (random): random concentration taken at least 24 hours after commencement of vancomycin. This is used for continuous infusions
- Steady-state area-under-the-curve (steady-state AUC): AUC calculated (using the AUC calculator) at least 24 hours after commencing vancomycin
- Concentration: measured amount of vancomycin (this guideline is referring to concentration in the blood). Referred to as ‘level’ in other guidelines
Vancomycin can be administered as an
- Intermittent infusion eg 1-hour infusions every 6, 8, 12 or 24 hours
OR - continuous infusion (over 24 hours)
Pharmacodynamic target exposure for vancomycin: AUC/MIC of 400- 650 mg/L.h
- Intermittent dosing
- Traditionally a trough concentration 10-20 mg/L has been used as a surrogate for the AUC (due to lack of an accessible calculator or easy way to calculate the AUC), however trough concentrations are not always an accurate correlate of AUC
- International guidelines now recommend using the steady-state trough concentration to calculate the AUC rather than using a trough concentration alone. Using the AUC target has been shown to reduce nephrotoxicity
- Continuous dosing
- A steady-state concentration (random) between 17-25 mg/L accurately correlates to an AUC 400-650 mg/L.h when continuous infusion is used. Therefore, the AUC is not required to be calculated
Dosing regimens
Patient age |
Dosing regimen |
Therapeutic drug monitoring target |
0-90 days |
Continuous infusion (recommended) |
Steady-state concentration 17-25 mg/L |
Intermittent dosing
If a continuous infusion cannot be used (eg due to limited intravenous line availability), use intermittent dosing using the online dosing calculator |
Steady-state AUC 400-650 mg/L.h
|
˃90 days |
Intermittent dosing (recommended) |
Steady-state trough concentration 8-15 mg/L |
Continuous infusion
Consider continuous infusion in critically ill patients or when unable to achieve therapeutic vancomycin concentrations with intermittent dosing. Seek specialist advice |
Steady-state concentration 17-25 mg/L |
Infants 0-90 days of age
Continuous infusion in infants 0-90 days of age
Dosing
Loading dose 15 mg/kg/dose IV (over 1 hour) followed by continuous infusion:
Serum creatinine (micromol/L) |
Corrected Gestational Age (CGA) |
Continuous infusion dose |
<40 |
≥40 weeks |
50 mg/kg/day |
<40 |
<40 weeks |
40 mg/kg/day |
40–60 |
All |
30 mg/kg/day |
>60* |
All |
20 mg/kg/day |
* >60 to the upper limit of normal for serum creatinine. For children with renal impairment, seek specialist advice for dosing
Switching from intermittent vancomycin dosing to continuous infusion:
- Commence at dose equivalent to total daily dose administered in the previous 24-hour period
- Continuous infusion can be commenced immediately after last intermittent dose is given
- Do not give a loading dose when switching to a continuous infusion
Therapeutic drug monitoring
Target exposure: steady-state concentration (random) 17–25 mg/L
- Collect sample for steady-state concentration 24-36 hours after start of infusion (with routine bloods where possible)
- Take sample from a different access point to where the vancomycin is being infused (taking a sample from a different lumen within the same line as the infusion could still result in a higher than expected concentration)
- If steady-state concentration is within target range, continue vancomycin infusion and repeat steady-state concentration 24 hours after first concentration
Dose adjustment
If steady-state concentration is outside therapeutic range, adjust dose according to the following formula:
Adjusted dose (mg/day) = last maintenance dose (mg/day) x (target concentration/last vancomycin concentration)
The maximum total daily dose should not exceed 80 mg/kg/day without seeking specialist advice
Example: if a 3 kg infant is prescribed 50 mg/kg/day and has a steady-state concentration of 13 mg/L
the adjusted dose = 150 mg x (20/13) = 230 mg/day (= 77 mg/kg/day)
Intermittent dosing in infants 0-90 days of age
Individualised dosing and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) with calculation of area under the curve (AUC) are to be done using the KidsCalc online vancomycin calculators. The calculators were developed by researchers at MCRI in collaboration with RCH and are based on a published population pharmacokinetic model
Seek specialist advice for dosing and TDM for the following infants, for whom the vancomycin KidsCalc calculators are not intended to be used:
- PMA <25 weeks
- Weight <500 grams
- Renal impairment
- Receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or renal replacement therapy
Dosing
Individualised dosing using KidsCalc Vancomycin intermittent dosing calculator for infants 0-90 days (target AUC of 500 mg/L.h) is based on the infant’s
- Postmenstrual age (PMA)(weeks) (same as corrected gestational age)
- Weight (kg)
- Serum creatinine (micromol/L)
Loading doses are not recommended for infants 0-90 days of age as they have been shown to increase the risk of renal impairment
Therapeutic drug monitoring
Target exposure: steady-state AUC 400-650 mg/L.h
- For intermittent dosing in infants 0-90 days, the AUC should be calculated each time a steady-state concentration is measured
Initial steady-state trough concentrations should be taken (and an AUC calculated) according to the following:
| Dosing frequency |
Timing of initial steady-state trough concentration |
6 hourly |
Before the 5th dose |
8 hourly |
Before the 4th dose |
12 hourly |
Before the 3rd dose |
18 hourly |
Before the 2nd dose |
24 hourly |
Before the 2nd dose |
- Steady-state trough concentration samples are to be taken approximately 30 minutes before the dose is due
- For patients with normal renal function, the next dose of vancomycin should be given at the scheduled time before the concentration is known
Calculate the AUC via KidsCalc Vancomycin AUC calculator for infants aged 0-90 days*, based on:
- PMA (weeks)
- Weight (kg)
- Serum creatinine (micromol/L)
- Dose (mg) and dosing interval (hours)
- Trough concentration taken at least 24 hours after commencing vancomycin or adjusting dose
*Do not use the AUC calculator if any of the following (Seek pharmacist or specialist advice)
- There have been missed doses in the 24 hours prior to the concentration being taken; OR
- The concentration was taken prior to reaching steady-state ie less than 24 hours after commencing vancomycin or adjusting the dose
Intermittent vancomycin dosing in infants 0-90 days of age
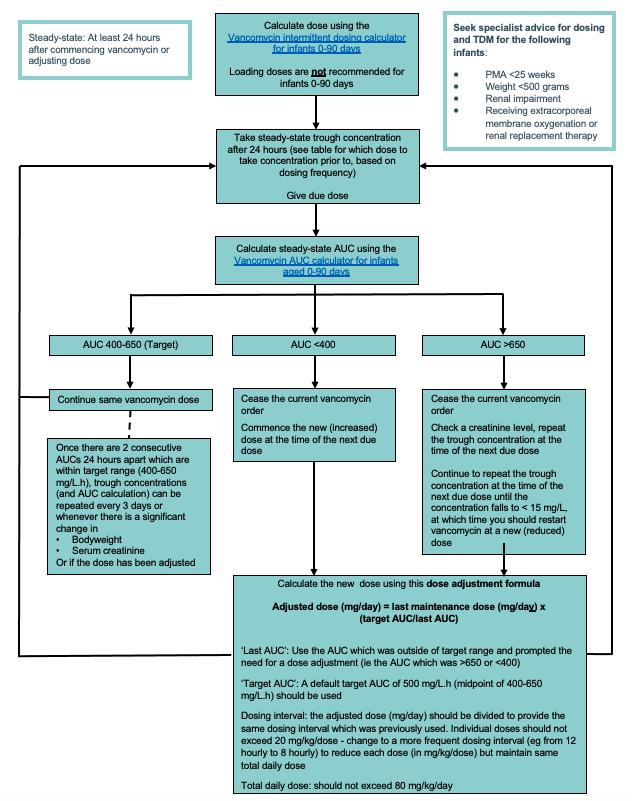
Example AUC > 650
3 kg infant with PMA 40 weeks is prescribed 50 mg 8 hourly (50 mg/kg/day) and has a steady-state trough concentration of 25 mg/L at 24 hours. This gives an AUC of 740 mg/L.h
- Cease the current vancomycin order and check creatinine
- Repeat trough concentration at time of next due dose (32 hours)
- The concentration taken at 32 hours is 14 mg/L, which is <15 mg/L, therefore vancomycin can now be re-started at a lower adjusted dose
- Adjusted dose = 150 mg x (500/740) = 101 mg/day = 34mg 8 hourly (the dose interval should not change)
RCH only: Contact the ward pharmacist or on-call pharmacist if assistance is required with dose adjustment or with the use of the initial dose, AUC or EMR dose adjustment calculators.
Infants and children > 90 days of age
Intermittent dosing in children > 90 days of age
Dosing
Usual starting dose: 15 mg/kg/dose (maximum 750 mg) every 6 hours
- The dosing interval should be 6 hourly; this is the only dosing interval with evidence for the steady-state trough concentration being used as an accurate correlate for AUC
- Use actual body weight for dose calculations, including obese patients, up to the maximum recommended doses
- For children with moderate to severe renal impairment, seek specialist advice for initial dosing
Therapeutic drug monitoring
Target exposure: steady-state trough concentration 8-15 mg/L
- Initial trough concentration should be taken prior to the 5th dose (ie 24 hours after commencing 6 hourly dosing)
- Steady-state trough concentration samples are to be taken approximately 30 minutes before the dose is due
- Steady-state trough concentration 8-15 mg/L correlates to vancomycin AUC 400-650 mg/L.h in children on 6 hourly dosing
Intermittent vancomycin dosing in children >90 days of age
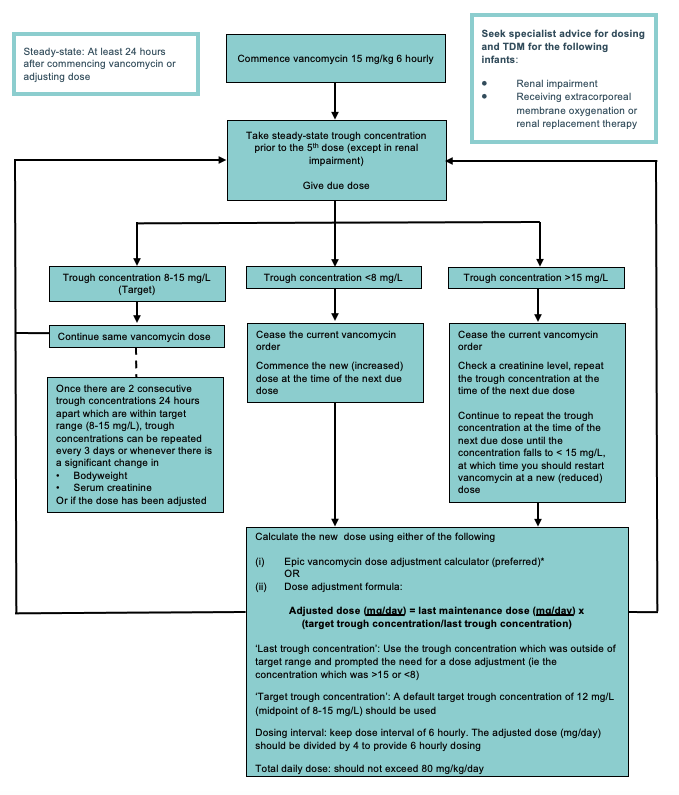
*Dose adjustment using Epic dose adjustment calculator: when using the calculator, use the original vancomycin concentration which was outside of target range ie the concentration which was >15 or <8 mg/L
Continuous infusion in children > 90 days of age
Seek specialist advice
Dosing
Initiating vancomycin treatment with a continuous infusion:
- Give loading dose 20 mg/kg over 1 hour, followed by continuous infusion
- Usual starting dose for continuous infusion is 60 mg/kg/day
Switching from intermittent vancomycin dosing to continuous infusion:
- Commence at dose equivalent to total daily dose administered in previous 24-hour period
- Continuous infusion can be commenced immediately after last intermittent dose is given
- Loading dose is not required
- The maximum total daily dose should not exceed 80 mg/kg/day without seeking specialist advice
Therapeutic drug monitoring
Target exposure: steady-state concentration (random) 17–25 mg/L
- Collect sample for steady-state concentration approximately 24 hours after start of infusion (with routine bloods where possible)
- If steady state concentration is within target range, continue vancomycin infusion and repeat steady-state concentration 24 hours after first concentration
Dose adjustment
If steady-state concentration is outside therapeutic range, adjust dose according to the following formula:
Adjusted dose (mg/day) = last maintenance dose (mg/day) x (target concentration/last vancomycin concentration)
The maximum total daily dose should not exceed 80 mg/kg/day without seeking specialist advice
Administration
Dilute to 5 mg/mL or weaker and infuse over at least 60 minutes (maximum rate 10 mg/minute)
Concentrations up to 10 mg/mL may be administered via a central line if necessary. The risk of infusion reactions is increased with higher concentrations
Adverse effects
Vancomycin is potentially nephrotoxic and ototoxic, especially when used in combination with other nephrotoxic or ototoxic agents (eg aminoglycosides) and in renal impairment
Rapid infusion may cause vancomycin infusion reaction (previously referred to as red man syndrome):
- flushing or rash on upper body and neck
- muscle spasm of chest and back
- fever
- hypotension
- itch
These features develop quickly and usually subside within an hour, but may persist for several hours in some cases
If symptoms of vancomycin infusion reaction occur:
- Cease infusion
- Check dose and infusion rate
- Wait for symptoms to resolve
- Further dilute infusion if possible
- Resume infusion at a reduced rate
- Document adverse reaction in patient notes and update their Allergies and Adverse Drug Reaction details
- Infuse subsequent doses over 90-120 minutes and consider administration of an antihistamine before future doses
Consider consultation with local paediatric team when
- Child with renal impairment
- Unable to achieve steady-state AUC or trough concentration within the target range
Consider transfer when
Child requiring care beyond the level of comfort of the local hospital
For emergency advice and paediatric or neonatal ICU transfers, call the Paediatric Infant Perinatal Emergency Retrieval (PIPER) Service: 1300 137 650
Last updated July 2024